The city of start-ups: Location determinants of start-ups in emergent industries in Barcelona
Coll, E. , Jové, E. i Teruel, Mercedes: “The city of start-ups”, Growth and Change
Several authors suggest that cities promote technology, innovation, and the growth of disruptive technologies (Bosma and Sternberg, 2014; Balland et al., 2020). In recent years, cities have become nursery start-ups and high-risk investments have shifted from the outskirts to the city center (Florida and Mellander, 2016). This is a common trend, observed not only in the United States, but in many major cities around the world (Florida, 2013; Florida and Mellander, 2016).
Among these, Barcelona occupies a prominent place internationally, just behind European cities such as London, Paris, Berlin and Amsterdam. Its growing popularity as a business center is due at least in part to the efforts made by the Generalitat in recent years to develop a rich and diverse ecosystem.
In recent years, Barcelona has been named World Mobile Capital (2012), European Capital of Innovation (2014) and first in the ranking of global smart cities (2015). In 2018, Barcelona was chosen as the third most attractive city for the founders (CITIE, 2015; Mobile World Capital Barcelona, 2018; Start-up Genome, 2017). Over these years, around 1,000 technology startups have been located in Barcelona.
Understanding the location of emerging firms has become a key issue as knowledge production is spatially limited (Baptista and Mendonça, 2010; Calcagnini et al., 2016; Florida and King, 2018; Moeller, 2014). Cities are the place where innovative innovation can thrive and contribute to the well-being of its citizens. Exploring how large urban areas drive innovation ecosystems provides valuable information for building resilient and sustainable spaces. This seems especially true for Barcelona, as its government aims to launch a global ecosystem of start-ups to attract more business, talent and investment as part of competition between the world's most dynamic and enterprising regions.
The effect of economic environment on the location of start-ups is highly significant for Creative, Ecological and Industry 4.0 start-ups. Although we expected to find a positive and significant effect for all type of emergent industries, these results may suggest that there are some external elements among the ones considered for the construction of the index that are less relevant for these industries.
FIGURE 1. Geographical distribution of start-ups by emergent industries (2012‒2015).
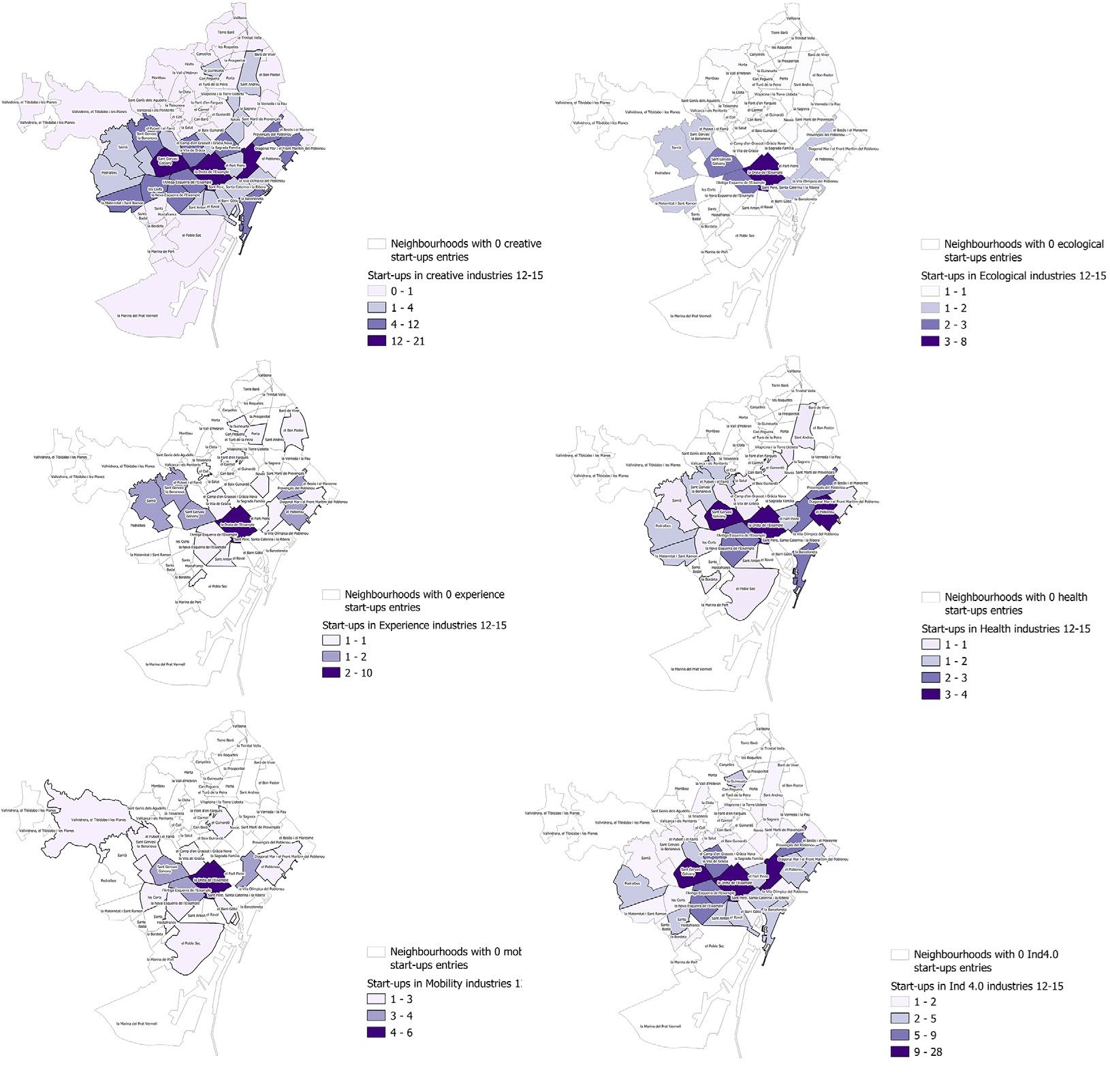
(a) Creative; (b) Ecological; (c) Experiences; (d) Health; (e) Mobility; (f) Industry 4.0.
Source: Prepared by the authors based on ACCIÓ data.
This article examines how local attributes, proximity to the elements of an entrepreneurial ecosystem (EE), and nearby economic activity influence the location of ambitious start-ups in Barcelona between 2012 and 2015.
To do this, we use microgeographic data from Barcelona start-ups provided by the Generalitat de Catalunya (ACCIÓ) and open data on the socio-economic composition of Barcelona's neighborhoods from the Department of Statistics of the Barcelona Council. In dealing with neighborhood effects and endogenity, our results suggest that location economies and proximity to EE elements are key factors in attracting start-ups to Barcelona neighborhoods.
These results are crucial in helping policymakers understand the location factors of emerging businesses in the city.

